We’ve rounded up the most incredible Medieval Shields that will ensure you stay safe during any conflict.
From the Kite Shield to the Heater Shield, these Middle Ages Best Battle Shields provided an unrivaled level of protection on the battlefield.
So read on and find out more about these amazing medieval shields that have been used for centuries!
A staple of the Middle Ages, the Kite Shield was a popular choice for soldiers due to its size and shape. This shield was much larger than the Heater Shield and was often used to cover the soldier from neck to ankle.

It formed a classic kite shape and was typically made from wood or metal, with a rounded top edge rather than being pointed like a kite.
The Kite Shield is featured on the Bayeux Tapestry and was also known as the tapering shield, It is distinguishable from other shields like The Buckler Shield, The Mantlet Shield, The Rondache Shield and The Targe shield by its large size and kite shape.

Though it wasn’t as effective as the Pavise shield, the Kite Shield offered adequate protection in battle and served as a symbol of strength and courage.
The Heater shield was a type of shield used widely by knights in the Middle Ages. It was a medium-sized shield, made of either wood or metal, and was slightly shorter than the Kite Shield.
This shorter size made it perfect for use by cavalry, who were able to maneuver around more easily than with the Heater shield.
The Heater shield was usually decorated with the coats of arms or heraldry of the holder, so that they could be easily identified in battle.

Additionally, this type of shield was often used in conjunction with other shields such as The
Buckler Shield
Pavise shield
Rondache Shield
Targe shield
Together, these shields provided great protection and gave the knight a better chance of survival.
The Rondache Shield, also known as the Roundel Shield, was one of the most popular medium-sized shields used in the Middle Ages. It was a circular shield that was constructed from wood and metal, with some shields featuring embossed leather, silver and gold, rope patterns or even nails.
This type of shield was widely used throughout Europe during the 16th century, and was especially favored by cavalry due to its portability and strong defensive capabilities.
The Rondache Shield was used for both defensive and offensive purposes; when in battle, this type of shield was typically held close to the body to deflect blows from enemies. This shield also worked great for parrying attacks from larger weapons such as spears and swords.
In addition, it provided additional protection against arrows, making it a great choice for soldiers looking to defend themselves on the battlefield.
When not in battle, the Rondache Shield could be seen in a variety of different settings. For example, it was often used in tournaments to test the skills of knights, while providing them with extra protection.
The Roundel Shield also made an appearance in ceremonies and processions, with some shields featuring intricate designs that signified a person’s rank or station in society.
Overall, the Rondache Shield was one of the most popular shields used during the Middle Ages. Its small size and strong defensive capabilities made it ideal for both defensive and offensive tactics on the battlefield, while its decorative nature made it a popular choice for ceremonies and tournaments alike.
It’s no wonder that this type of shield remains a favorite among historical re-enactors today!
The Pavise shield was a large defensive shield, that provided superb protection to medieval archers, in was commonly used by medieval crossbowmen, it was large and rectangular and had similarities to the larger Manlet shield, these type of shields were often called collectively as wall shields.
It was used from the 14th century, and was typically made of wood or metal. It could protect the holder’s entire body and was often accompanied by a Pavise-bearer, whose job was to hold the shield for the archers.
Like the Kite shield, Pavise shields could have heraldry on the front of them. The shield featured curved sides that allowed it to be leaned against walls and other structures when not in use, which gave rise to its name.
It was heavier than other shields such as the Heater Shield, Buckler Shield, and the Targe Shield, but offered superior protection against attacks.
All of these shields were vital for protecting Medieval soldiers in battle, and helped to ensure their safety and success in battle.
The Buckler shield is a small, round shield made of iron or metal that was used during the Middle Ages. It was lightweight and hung from a soldier’s belt, making it an ideal choice for hand-to-hand combat.
Despite its size, the Buckler shield could still provide some protection in battle against other weapons such as swords, arrows, and spears.
The Buckler shield was also much lighter than other shields of the period such as the Kite Shield, the Heater Shield, the Pavise shield, the Rondache Shield, and the Targe shield.
All of these other shields were much bigger than the Buckler shield, soldiers could carry Buckler shields comfortably into battle without being weighed down.
The targe shield is a round shield that is similar to the Buckler shield, but it is larger being described as a medium to large shield.
It was widely used by Scottish highlanders during the 15th century to protect themselves from attack and was often adorned with studded nails punched into the front in a decorative pattern.
This shield was typically smaller than other shields such as the Kite Shield, Heater Shield, Pavise Shield, Rondache Shield, Mantlet Shield and Bouche Shield, but still provided adequate protection for the wearer.
It is considered to be one of the best defensive shields of its time and is still highly regarded for its effectiveness even today.
The Bouche Shield was a type of shield commonly used during the Middle Ages, particularly for jousting tournaments. This shield is slightly different than others of its kind, as it has a ridge in the centre of its front plate which is designed to deflect weapons away from the knight.
The Bouche Shield had a unique designed that made it a perfect companion for a knights lance which could be rested into a groove at the top of a frontal plate.
The Bouche Shield a great option for those who wish to fight with a lance.
The Bouche Shield has similarities with other popular shields of the Middle Ages, such as The Buckler Shield, The Heater Shield, The Kite Shield, The Mantlet Shield, The Pavise shield, The Rondache Shield, and The Targe shield.
Each of these shields offers varying levels of protection and defence, making them ideal for different types of combat situations.
The Mantlet Shield is a large and wooden shield, similar to the Pavise shield. The main purpose of this shield was to protect the holder from incoming arrows. Its design is unique in that it features an arrow slit in the front, allowing the holder to fire out and also blocking arrows coming in.
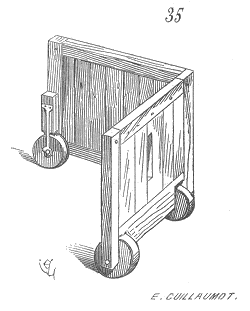

This makes it ideal for both offensive and defensive purposes, however, the Mantlet shields were vulnerable to attack from ground troops. To make up for this deficiency, the shield could be moved on wheels.
The Mantlet Shield was often reffered to as a wall shield, it was commonly used by medieval archers such as crossbowmen who would crouch behind it and it offered them perfect protection from incoming missiles when re-loading their crossbows, which was a slower process than for longbowmen who could fire of their arrows more rapidly.
The shields used in Medieval times were not just pieces of metal to block arrows and swords. They were also works of art, that served as symbols of pride and identity. The variety of designs and shapes, from the Kite shield to the Heater Shield, show the complexity and the importance of shield craftsmanship in the Middle Ages.
Most shields featured a handle called an Enarmes, which was either gripped by hand or arm and attached to the back of the shield by rivets and washers.

This allowed for maneuverability and accuracy during battle. Another interesting aspect of these shields is their materials. Most were made of wood and metal, while some featured intricate designs with colorful fabrics.
The Buckler Shield was a small round shield, usually made of metal and often decorated with emblems or family crests. It was light and easy to carry, but its size offered limited protection.
The Rondache Shield, or Roundel Shield, was similar to the buckler but larger and oval in shape. It was made from leather covered in metal plates and could withstand stronger blows from weapons.
The Targe Shield was large, circular or oval and often had decorative paintings or carvings. It was especially effective against arrows, due to its shape which deflected them away from the body.
The Bouche Shield was a pointed shield that offered good protection against swords and spears, due to its sharp point.
The Pavise shield was a large rectangular shield made from wood and sometimes covered in leather. It was often held upright with a stick on the ground so it could provide cover for archers and crossbowmen.
The Mantlet shield was similar in size to the Pavise but was able to stand alone due to its curved shape.
Overall, Medieval shields provided much needed protection during battles and were essential tools in Medieval warfare. Their diversity in design reflects both a practical need for various types of shields, as well as the creativity of Medieval craftsmen.
The medieval shields used by knights and warriors during the Middle Ages were made by a wide variety of craftsmen and artisans.
Shields came in all shapes and sizes, from the small Buckler Shield to the large Kite Shield, the Heater Shield, the Rondache Shield or Roundel Shield, the Pavise Shield, the Targe Shield, the Bouche Shield and the Mantlet Shield.
Many shields were handcrafted by local blacksmiths, while others were imported from foreign countries. It is believed that shields were used as early as the 10th century BC, but it wasn’t until the 5th century AD that they began to be made more regularly.
During this period, craftsmen took great care in the production of shields and would often spend days or weeks creating one.

They would use a range of materials, including iron, leather, bronze, and wood, to make their shields strong and durable. Shields were also decorated with various symbols and motifs to signify their owner’s allegiance.
For example, The Buckler Shield was often decorated with a lion rampant or a griffon crest.
Medieval shields were truly works of art and played an important role in battle.