The Middle Ages (c. 500–1500 CE), also known as the medieval period, was a transformative era that shaped the course of world history. During these thousand years, empires rose and fell, religions spread, and societies experienced incredible cultural, scientific, and political developments. From the fall of the Western Roman Empire to the rise of powerful kingdoms, from the crusades and the Black Death to the invention of the printing press, this period witnessed events that had a lasting impact on Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
Understanding the most significant events of the Middle Ages helps us appreciate how medieval societies laid the foundations for the modern world. This article presents a comprehensive timeline of 100 key events, providing a global perspective that highlights the political, religious, technological, and cultural milestones of the medieval era.

500–600 CE
527 – Justinian I becomes Byzantine Emperor → Initiates legal reforms and commissions the Hagia Sophia.
529 – Benedict of Nursia founds Monte Cassino → Foundation of Western monasticism.
532 – Nika Riots in Constantinople → Massive urban revolt nearly topples Justinian.
533 – Belisarius reconquers North Africa → Temporary revival of Roman control.
537 – Hagia Sophia completed → Icon of Byzantine architecture.
563 – St. Columba establishes Iona monastery → Spreads Christianity to Scotland.
570 – Birth of Muhammad → Prophet of Islam, whose teachings reshape the world.

600-700 CE
622 – Hijra of Muhammad to Medina → Marks the beginning of the Islamic calendar.
632 – Death of Muhammad → Expansion of Islamic Caliphates begins.
636 – Battle of Yarmouk → Arabs defeat Byzantines, securing Syria.
651 – Fall of the Sassanian Empire → Persia absorbed into Islamic world.
663 – Buddhist Council in Japan → Institutionalizes Buddhism in East Asia.
680 – Battle of Karbala → Sunni–Shia split solidifies in Islam.
698 – Carthage captured by Arabs → North Africa fully integrated into Dar al-Islam.

700–800 CE
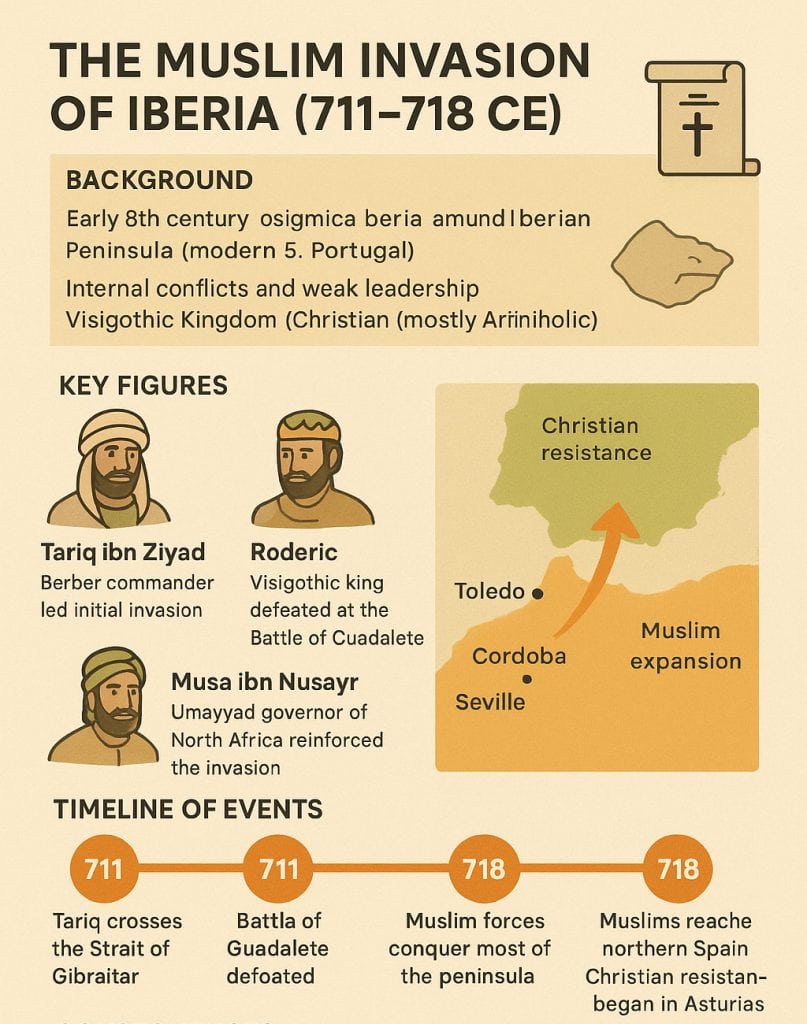
711 – Muslim invasion of Iberia → Umayyads establish Al-Andalus.
732 – Battle of Tours → Charles Martel halts Muslim expansion into France.
750 – Abbasid Caliphate established → Islamic Golden Age begins.
751 – Battle of Talas → Arabs defeat Tang, paper technology spreads west.
768 – Charlemagne crowned King of the Franks → Expands Frankish Empire.
793 – Viking raid on Lindisfarne → Start of Viking Age.
800–900 CE
800 – Charlemagne crowned Holy Roman Emperor → Symbol of Christian empire revival.
843 – Treaty of Verdun → Carolingian Empire divided into three kingdoms.
864 – Christianization of Bulgaria → Expands Orthodox influence.
868 – Diamond Sutra printed in China → World’s earliest dated printed book.
870 – Rise of Kievan Rus’ → Eastern Slavic state begins.
878 – Battle of Edington → Alfred the Great defeats Vikings in England.
896 – Death of Formosus sparks “Cadaver Synod” → Papal politics turn violent.

900–1000 CE
911 – Viking leader Rollo granted Normandy → Birth of Normandy.
919 – Otto I elected King of East Francia → Later founder of Holy Roman Empire.
929 – Caliphate of Córdoba established → Height of Islamic Spain.
960 – Song Dynasty established in China → Era of innovation and commerce.
962 – Otto I crowned Holy Roman Emperor → Empire consolidated.
987 – Hugh Capet crowned in France → Capetian dynasty begins.
999 – Gerbert of Aurillac becomes Pope Sylvester II → Promotes science and learning.

1000–1100 CE
1000 – Leif Erikson reaches North America → Norse exploration of Vinland.
1016 – Canute becomes King of England → North Sea Empire formed.
1054 – The Great Schism → Split between Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches.
1066 – Norman Conquest of England → William the Conqueror crowned at Hastings.
1071 – Battle of Manzikert → Byzantines defeated by Seljuks.
1095 – Pope Urban II calls First Crusade → Launch of Crusader movement.
1099 – Crusaders capture Jerusalem → Establishment of Crusader states.

1100–1200 CE
1122 – Concordat of Worms → Ends Investiture Controversy.
1147 – Second Crusade begins → Failure in the Holy Land.
1150 – Rise of Gothic architecture → First Gothic cathedral at Saint-Denis.
1170 – Murder of Thomas Becket → Clash of church and monarchy in England.
1187 – Saladin retakes Jerusalem → Sparks Third Crusade.
1192 – Kamakura Shogunate established → First shogunate in Japan.

1200–1300 CE
1206 – Genghis Khan elected Great Khan → Mongol Empire begins.
1215 – Magna Carta signed in England → Foundation of constitutional law.
1227 – Death of Genghis Khan → Empire divided among heirs.
1241 – Mongol invasion of Europe halted at Legnica → Mongol expansion checked.
1258 – Mongols sack Baghdad → Abbasid Caliphate falls.
1271 – Marco Polo begins travels to Asia → Expands European knowledge.
1291 – Fall of Acre → End of Crusader states in the Levant.

1300–1400 CE
1302 – Dante begins writing Divine Comedy → Cornerstone of Italian literature.
1315–1317 – Great Famine in Europe → Millions perish.
1324 – Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca → Mali’s wealth amazes the world.
1337 – Start of the Hundred Years’ War → England vs. France rivalry.
1347–1351 – Black Death ravages Europe → Up to half of population dies.
1381 – English Peasants’ Revolt → Challenges feudal order.
1389 – Battle of Kosovo → Key clash between Ottomans and Balkan states

1400–1500 CE
1402 – Battle of Ankara → Timur defeats Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I.
1405 – Zheng He begins first voyage → Chinese maritime exploration expands Indian Ocean trade.
1410 – Battle of Grunwald/Tannenberg → Polish-Lithuanian forces defeat Teutonic Knights.
1415 – Battle of Agincourt → English longbowmen defeat French knights.
1419 – Hussite Wars begin → Religious reform in Bohemia.
1429 – Siege of Orléans → Joan of Arc lifts siege, turning the Hundred Years’ War.
1431 – Execution of Joan of Arc → French heroine martyred.
1433 – End of Ming treasure voyages → China retreats from large-scale maritime exploration.
1438 – Rise of Inca Empire under Pachacuti → Foundation of one of the largest pre-Columbian states.
1440 – Gutenberg Bible printed → Launch of mass-produced books in Europe.
1444 – Battle of Varna → Ottoman expansion continues in the Balkans.
1450 – Gutenberg Bible printed → Launch of mass-produced books in Europe.
1453 – Battle of Castillon → End of Hundred Years’ War; France victorious.
1453 – Fall of Constantinople → End of Byzantine Empire; Ottomans rise.
1460 – Edo period foundations in Japan → Centralization leading to Tokugawa era.
1469 – Marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella → Spain unified politically and religiously.
1478 – Spanish Inquisition begins → Religious consolidation and persecution.
1485 – Battle of Bosworth Field → Tudor dynasty begins in England.
1490 – Height of Aztec Empire under Ahuitzotl → Expansion and consolidation of Mesoamerican power.
1492 – Columbus reaches the Americas → Global Age of Exploration begins.
1492 – Fall of Granada → End of Muslim rule in Iberia.
1494 – Treaty of Tordesillas → Spain and Portugal divide New World.
1498 – Vasco da Gama reaches India → Establishes direct maritime trade route from Europe to Asia.
1499 – Amerigo Vespucci begins voyages → European exploration of South America.

Additional Global Coverage
1200 – Delhi Sultanate established → Muslim rule begins in northern India.
1235 – Mali Empire founded under Sundiata Keita → West African kingdom rises to power.
1258 – Mongol invasion of Persia → Mongol control expands through Middle East.
1279 – Yuan Dynasty ends; Ming Dynasty begins → Transition of power in China.
1325 – Founding of Tenochtitlan → Capital of the Aztec Empire in Mexico.
1325–1345 – Decline of Maya city-states → Major cultural and political shifts in Mesoamerica.
1340s – Spread of plague in Africa and Middle East → Extends Black Death impact beyond Europe.
1350 – Rise of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe → Flourishing trade and architecture in Southern Africa.
1400 – Timurid Renaissance in Persia and Central Asia → Advances in art, science, and architecture.
1438 – Rise of Inca Empire under Pachacuti → Foundation of one of the largest pre-Columbian states.
1453 – Fall of Constantinople → End of Byzantine Empire; Ottomans rise.
1460 – Edo period foundations in Japan → Centralization leading to Tokugawa era.
1485 – Battle of Bosworth Field → Tudor dynasty begins in England.
1492 – Columbus reaches the Americas → Global Age of Exploration begins.
1492 – Fall of Granada → End of Muslim rule in Iberia.

The Middle Ages were far from a static or “dark” period; they were an era of innovation, conflict, and transformation. From the Viking raids and Mongol conquests to the rise of empires in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, these events shaped not only their regions but also the broader trajectory of human civilization. By exploring these 100 pivotal events, we can see the interconnectedness of global history and understand how medieval societies influenced politics, culture, religion, and technology for centuries to come. This timeline of the Middle Ages offers a window into a world of resilience, creativity, and change, reminding us that the medieval period was a foundation upon which the modern world was built.
1. What is the Middle Ages period?
The Middle Ages, also known as the Medieval period, lasted from roughly 500 to 1500 CE, bridging the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the beginning of the Renaissance.
2. Why is the Middle Ages important in history?
The Middle Ages shaped modern Europe through key developments in politics, religion, culture, and technology, including the rise of kingdoms, the spread of Christianity, and early universities.
3. What were some major events in the Middle Ages?
Significant events include the fall of Rome, the rise of the Byzantine Empire, the Viking invasions, the Crusades, the Black Death, and the Hundred Years’ War.
4. How did the Middle Ages influence modern society?
The Middle Ages laid the foundation for modern law, government, architecture, education, and science, influencing how societies developed in Europe and beyond.
5. What is a complete timeline of the Middle Ages?
A complete timeline covers 500–1500 CE and includes political, religious, cultural, and technological milestones that shaped the medieval world.
6. Who were key figures of the Middle Ages?
Notable figures include Charlemagne, William the Conqueror, Joan of Arc, and Geoffrey Chaucer, each playing a pivotal role in European history.
7. How can I learn more about medieval history?
You can explore medieval history through books, documentaries, online courses, and historical timelines that detail important events and figures from the period.





