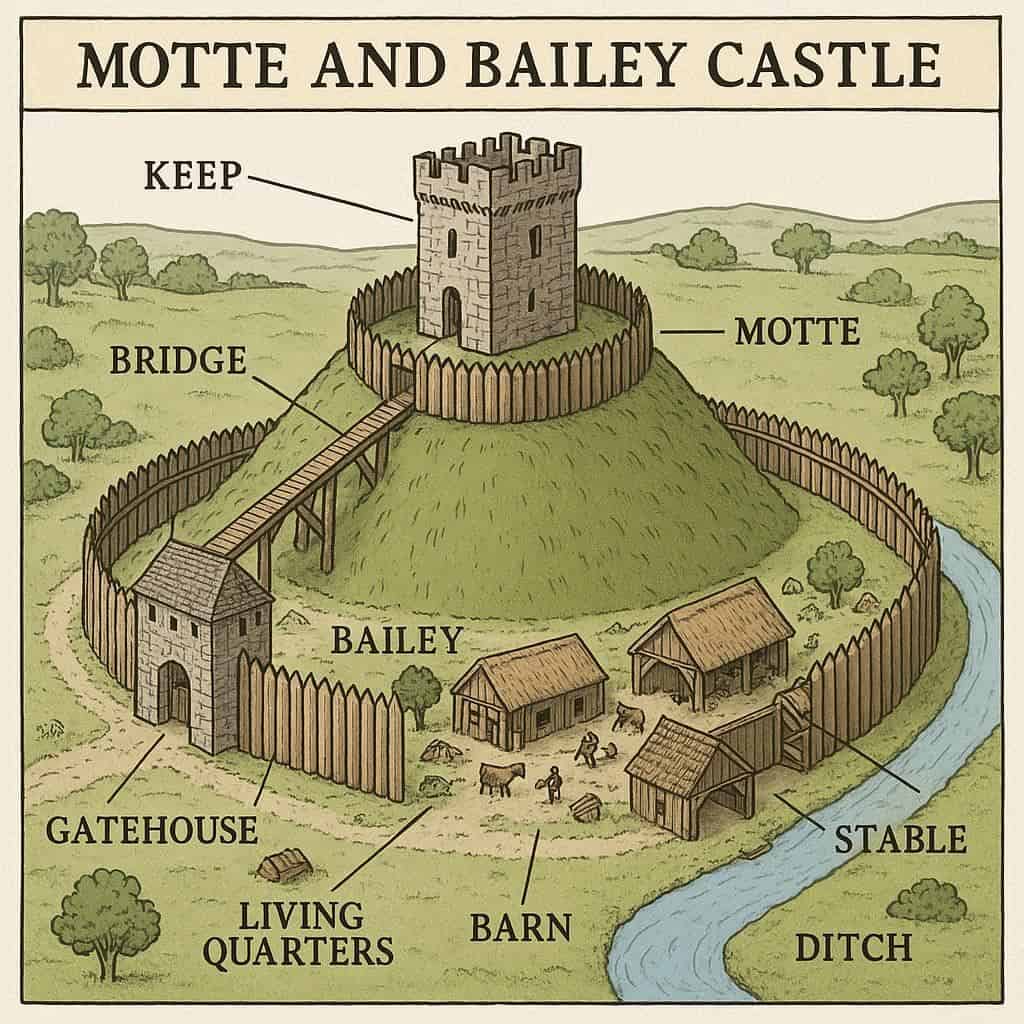
Motte and bailey castles were a revolutionary form of fortification introduced by the Normans in the 11th century, quickly transforming medieval warfare and defense. Characterized by a wooden or stone keep perched atop a raised earthwork called the motte, alongside an enclosed courtyard known as the bailey, these castles combined speed of construction with effective defense. Their design allowed Norman rulers to establish control over newly conquered lands swiftly, serving as both military strongholds and administrative centers during a turbulent period of history.
The Normans
Normans is a term that derives from “Norsemen”, Normans were originally the descendants of the Vikings who arrived in continental Europe during the Viking Age. During the 10th century, Vikings raids gave way to permanent Viking settlements in what was later the Duchy of Normandy.

Inspired by the castles that were built by the Franks in Francia, the Normans developed their own style of building castles which is known today as the ‘motte and bailey’, style castle. From the 10th century onward these types of castles started popping up in Europe on all fronts, they started appearing in the Holy Roman Empire during the 11th century.
What is a Motte & Bailey Castle?
A motte and bailey castle is a fortified structure built with a wooden or stone keep which was situated on the top of a raised dirt mound called a motte and accompanied by a protective ditch with its own palisade which surrounds the courtyard which is called the bailey.

Why Were Motte & Bailey’s Castles Built?
During the medieval period, having anything to protect an important location was always welcome, especially if it was cheap and easy to make. Motte and bailey castles fitted the bill as they were easy to build, even with unskilled labour, and yet still provided a very formidable defence.

During the Norman invasion of England in 1066, motte and bailey castles were introduced to this territory and rapidly started appearing in England, Wales, Scotland, and Ireland during the 12th and 13th centuries.
Motte & Bailey Castle Defences
The defence that the castle design provided, at that time, was advanced compared to previous castle designs. The Normans were able to build a network of castles across England and other lands such as Sicily quickly which enabled them to contain uprisings and expand their empire.

Stone Motte & Bailey Castles
Earlier castles of this type were constructed of wood as the medieval period progressed more stone was used until they became the complete stone castles we see today.

Another reason that stone was used was because of the advancement of siege weapons and tactics that nullified the defences of wooden structures.

Around the start of the 12th century, wood was no longer used and all the existing castles were either upgraded to stone keeps or were abandoned.

Castle design would advance even further as the medieval period progressed with moats, arrowslits, gatehouses, round towers, and murder holes added to these already formidable stone structures and this led to the creation of the mighty concentric castle with its multiple defensive walls!

End of the Motte & Bailey Castle
The motte and bailey castle provided formidable defense against attackers during the earlier stages of the medieval period and as time passed by during the middle ages they were either neglected or turned into stone castles that held the same design.

🏰 Frequently Asked Questions about Motte & Bailey Castles
What is a motte-and-bailey castle?
A motte-and-bailey castle was an early type of **fortified structure** with a wooden or stone keep on a raised mound (the motte) and a fenced courtyard (the bailey).
Who introduced motte-and-bailey castles to England?
They were introduced by the **Normans** after the conquest of England in 1066, led by William the Conqueror.
Why were motte-and-bailey castles popular?
They were **quick to build**, provided immediate defense, and allowed Normans to establish control rapidly across England.
What materials were used to build them?
Most early motte-and-bailey castles were made of **timber**, though some were later rebuilt in stone for durability.
What was the role of the motte?
The motte, a raised mound of earth, supported a **keep or tower**, giving defenders a height advantage over attackers.
What did the bailey contain?
The bailey enclosed essential buildings such as **barracks, stables, workshops, and living quarters**, protected by a wooden palisade and ditch.
Why did motte-and-bailey castles decline?
They declined by the 12th century as **stone castles** replaced timber structures, offering greater strength against fire and siege weapons.






